Table Of Contents
Analyzing Your Data
Data analysis forms the bedrock of effective analytics and reporting. It involves the careful examination of data sets to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. Employing various statistical methods and analytical tools can enhance the understanding of complex data. Ensuring that the right questions are posed before diving into the data is essential, as this helps to maintain focus and relevance in the findings.
Moreover, leveraging software applications that provide capabilities for data mining and predictive analytics can streamline the analysis process. Using these tools, analysts can uncover insights that may not be readily apparent. The integration of qualitative and quantitative data can lead to a more comprehensive view, allowing for deeper insights that inform decision-making. This level of analysis is critical for delivering actionable insights in the realm of analytics and reporting.
Techniques for Data Interpretation
Interpreting data effectively is crucial for successful analytics and reporting. Various techniques can be employed to draw meaningful insights from complex datasets. One approach is to use statistical analysis, which involves applying mathematical frameworks to summarise and understand the data patterns and trends. Techniques like regression analysis or cluster analysis can uncover relationships and groupings within the data, providing a clearer perspective on what the results indicate regarding the subject matter.
Another valuable method for data interpretation is to utilise storytelling through data. This involves contextualising the data within a narrative that highlights the key findings. Incorporating real-world examples or case studies can make the insights more relatable and easier to grasp. By weaving the data into a cohesive story, it can resonate with stakeholders and encourage informed decision-making, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of analytics and reporting.
Creating Insightful Reports
Effective reporting is integral to the process of analytics and reporting. A well-structured report provides clarity and creates a narrative that can be easily understood by various stakeholders. It is essential to determine the audience for the report, as this influences the level of detail and the type of language used. Customising reports to meet the needs of different stakeholders helps ensure that the insights derived from the data are communicated clearly and are actionable.
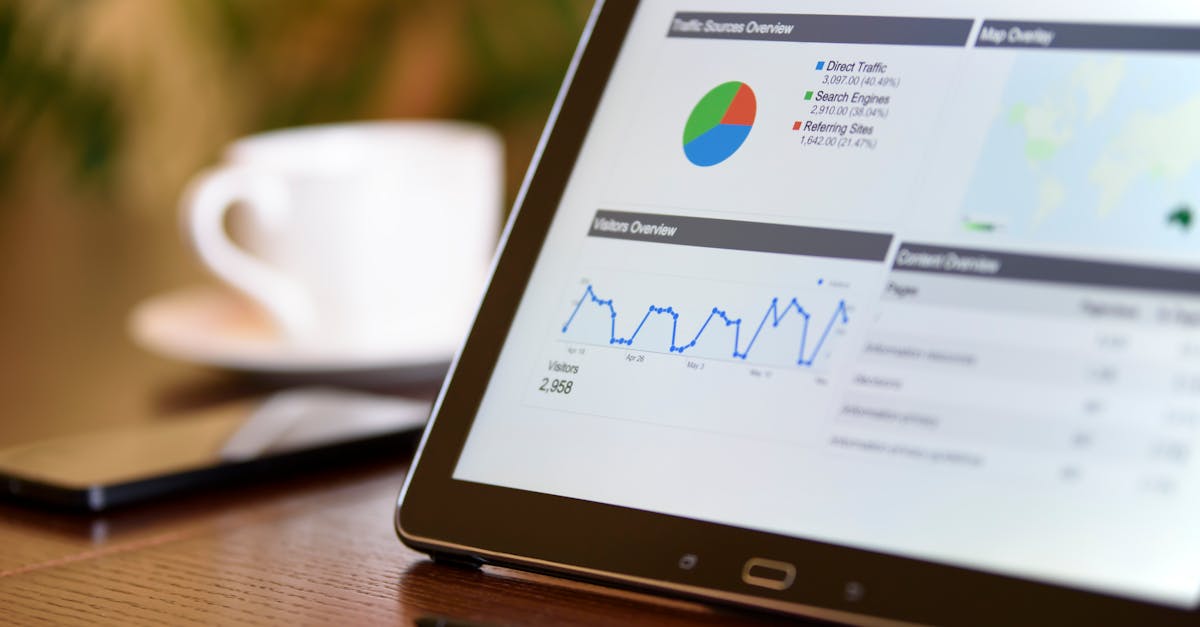
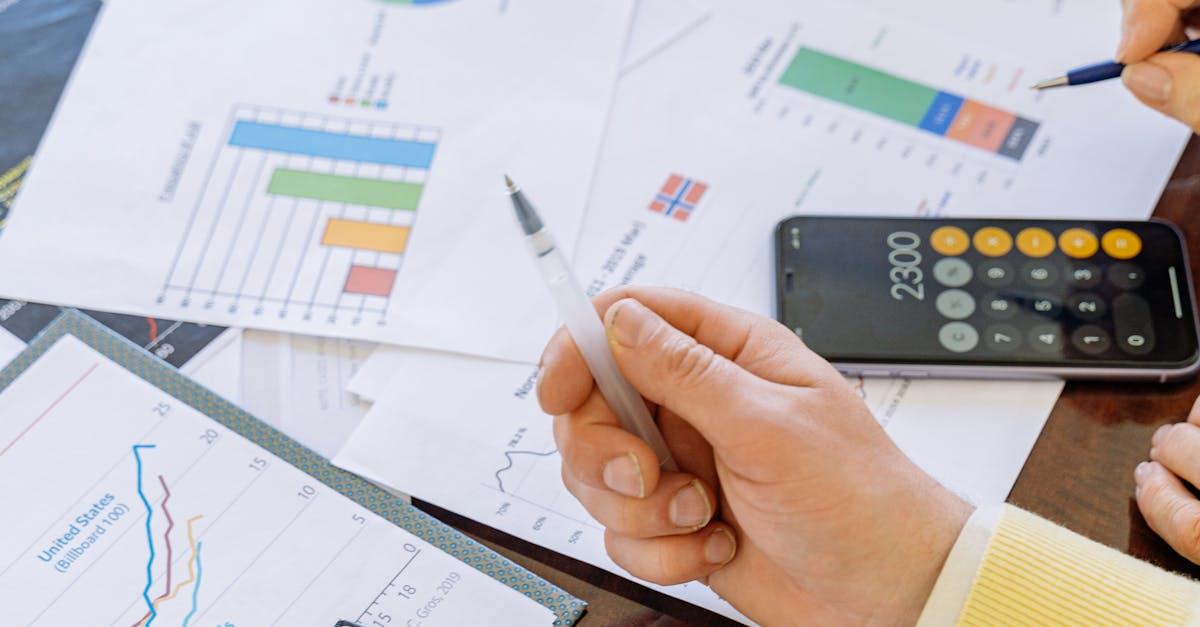
Incorporating visual elements can significantly enhance the impact of a report. Charts, graphs, and tables break up text and provide a visual representation of the data, making complex information more digestible. Additionally, including a summary of key findings and recommendations at the beginning allows readers to grasp the main insights quickly. By focusing on clarity and relevance, reports can serve as valuable tools in the analytics and reporting process, guiding decision-making and driving organisational strategies.
Essential Elements of a Good Report
A good report is built on clarity and conciseness, ensuring that the audience can easily grasp the essential findings. Each section should have a clear purpose, guiding the reader through the analytics and reporting process. Including a brief executive summary at the beginning provides a snapshot of the main insights, helping stakeholders understand the overarching conclusions at a glance. Well-defined headings and bullet points also aid readability, allowing readers to navigate the report effortlessly.
Equally important is the use of relevant data visualisations. Charts, graphs, and tables can transform complex data into easily digestible formats, making patterns and trends immediately apparent. It is essential that these visuals are accurately labelled and properly sourced to maintain credibility. Providing context around the visuals can enhance understanding, linking back to the analytics and reporting narrative to ensure every element serves its purpose in conveying the key messages.
Visualising Data Effectively
Effective data visualisation can significantly enhance the interpretation of complex datasets in analytics and reporting. By employing various graphical formats, such as bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts, analysts can convey insights more powerfully than through numbers alone. Selecting the right type of visual representation is crucial, as it must reflect the nature of the data and the story you aim to tell. Colour schemes and design elements can further influence the clarity and appeal of the visuals, ensuring they engage the audience’s attention while facilitating understanding.
Choosing the proper tools can make a notable difference in the quality of your data visualisations. Software such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio offers versatile options for creating dynamic and interactive reports. These platforms allow users to manipulate data in real-time, exploring different dimensions and metrics seamlessly. Incorporating visualisation best practices ensures that the representations are not only aesthetically pleasing but also accurate and informative, playing a vital role in successful analytics and reporting.
Tools and Techniques for Visualisation
Visualising data effectively is crucial for making complex information accessible and understandable. There are many tools available that cater to different analytics and reporting needs. Popular options like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio allow users to create interactive dashboards and visually appealing charts. These platforms often feature drag-and-drop functionalities, making them user-friendly for both beginners and seasoned analysts.
In addition to dedicated software, various programming libraries such as Matplotlib, Seaborn, and D3.js provide a more customisable approach to visualisation. These tools enable deeper manipulation of data and foster creativity in the presentation of insights. Effective visualisation enhances storytelling in analytics and reporting, facilitating clearer communication of findings to stakeholders. By choosing the right tools and techniques, analysts can create visuals that not only inform but also engage their audience.
FAQS
What is the first step in analysing data?
The first step in analysing data is to clearly define your objectives and the questions you want to answer, ensuring you understand the context of the data.
What are some common techniques for data interpretation?
Common techniques for data interpretation include statistical analysis, trend analysis, correlation analysis, and using data visualisation tools to highlight key patterns.
What essential elements should be included in a good report?
A good report should include a clear title, an executive summary, methodology, key findings, visual aids, conclusions, and recommendations.
How can I effectively visualise my data?
You can effectively visualise your data by using charts, graphs, and infographics that best represent the information, ensuring they are clear and easy to understand.
What tools can I use for data visualisation?
Some popular tools for data visualisation include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Google Data Studio, and Excel, each offering various features for creating compelling visuals.