Table Of Contents
Interpreting Qualitative Data
Interpreting qualitative data involves analysing non-numerical information to uncover insights that quantitative data may overlook. This process often requires careful examination of responses from interviews, surveys, or open-ended questions. Identifying the subtleties in language, tone, and context can reveal deeper meanings. It’s crucial to approach this analysis with a clear framework. This can help maintain focus on the objectives of the research, ensuring that the analysis aligns with the broader narrative and goals of the report.
Engaging with the data through methods like thematic analysis enhances the understanding of underlying sentiments and user experiences. The iterative nature of qualitative analysis means revisiting the data multiple times. This provides a comprehensive view rather than a superficial interpretation. Incorporating tools from Analytics and Reporting can streamline this process, enabling analysts to organise findings effectively and illustrate how they connect to the main themes. The goal is to transform raw data into valuable insights that inform decision-making and strategy.
Identifying Themes and Patterns
Identifying themes and patterns within qualitative data plays a crucial role in the Analytics and Reporting process. This method involves sifting through the data to uncover recurring ideas, concepts, or sentiments that emerge from participants’ responses. By carefully examining the text, researchers can highlight significant trends and insights that inform broader conclusions. This stage requires a keen eye, as well as a thoughtful approach to distinguish between trivial observations and meaningful patterns that hold relevance to the study’s objectives.
Another effective strategy entails grouping similar data points or responses together, which can enhance understanding of the overall narrative. Using coding techniques, analysts can tag phrases or sentences that reflect similar themes, enabling an easier workflow when synthesising information. Through this structured approach, patterns become more apparent, providing a clearer roadmap for further analysis. Ultimately, recognising these themes and patterns is instrumental for ensuring the integrity of the final report and enriching the findings provided in the Analytics and Reporting phase.
Comparing Against Benchmarks
To effectively measure performance, organisations can benefit from comparing their findings against established benchmarks. This practice allows for a clearer understanding of an entity’s standing within its industry or sector. By utilising Analytics and Reporting tools, stakeholders can identify gaps in performance and areas for potential improvement. Such comparisons provide context for qualitative insights, making it easier to pinpoint strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors or industry standards.
Setting relevant benchmarks is crucial in this evaluation process. These standards should align with the goals of the analysis and reflect realistic expectations based on historical data or industry norms. Involving a comprehensive approach to Analytics and Reporting ensures that the benchmarks selected are both meaningful and actionable. This alignment allows for a more robust interpretation of the data, ultimately guiding strategic decisions based on solid performance comparisons.
Setting Relevant Standards for Evaluation
Establishing relevant standards for evaluation is crucial in the analysis process. These standards should align with the specific objectives of the report while considering the expectations of stakeholders. By defining clear metrics and benchmarks, analysts can ensure a more objective assessment of performance. This structured approach allows for a focused interpretation of results, providing insights that are both actionable and aligned with broader organisational goals.
Utilising analytics and reporting tools can significantly enhance the setting of these standards. These tools provide the ability to compare results against industry benchmarks or historical data, facilitating an informed evaluation process. By leveraging quantitative and qualitative data, stakeholders can develop a comprehensive understanding of performance gaps and areas of success. Establishing these relevant standards not only supports accountability but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organisation.
Visualising Findings
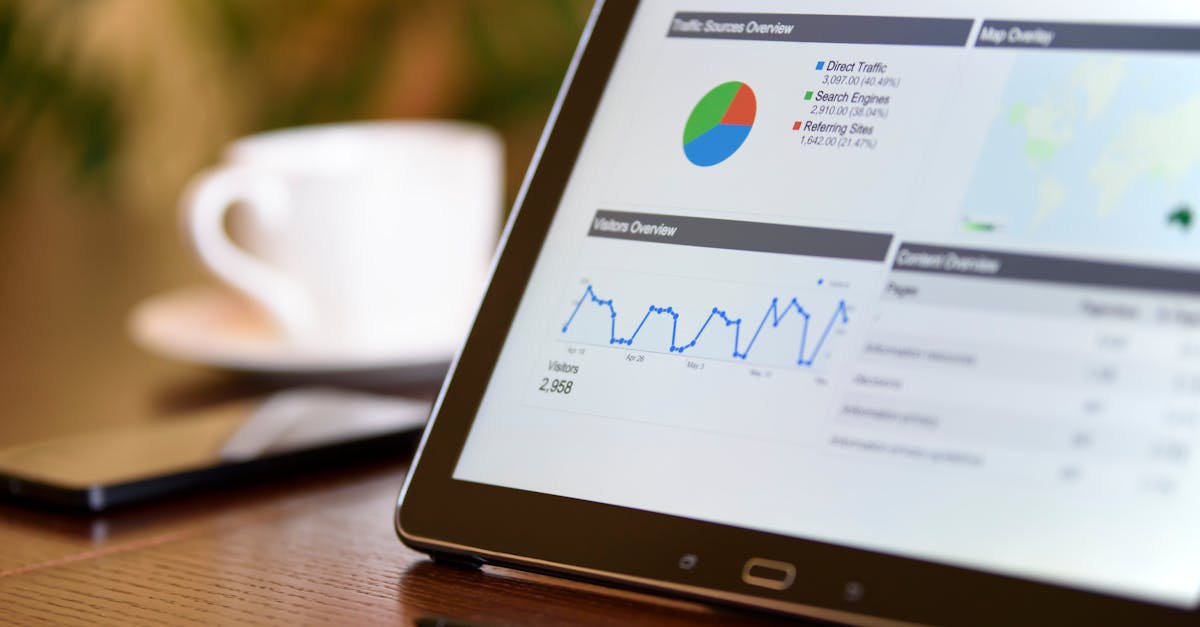
Visualising findings is essential in making complex data comprehensible. Effective visual representations can highlight key insights and enable stakeholders to grasp critical information quickly. Tools such as charts, graphs, and infographics transform raw data into understandable formats that aid in decision-making.
In the realm of Analytics and Reporting, visualisations not only enhance clarity but also facilitate comparisons across various metrics. By choosing appropriate visualisation techniques, analysts can illustrate trends over time or showcase relationships between different variables. This approach ensures the findings resonate with the intended audience and support a well-informed analysis.
Creating Effective Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs serve as powerful tools for transforming complex data sets into digestible visual formats. When creating effective visuals, clarity should be the primary goal. Selecting the appropriate type of chart depends on the nature of the data being represented. Bar graphs effectively depict comparisons among discrete categories, while line graphs reveal trends over time. Pie charts, although sometimes criticised for their inability to showcase detailed differences, can effectively represent parts of a whole when employed judiciously.
Incorporating key elements such as titles, labels, and legends enhances the accessibility of visual data. Analysts should focus on colour contrasts to ensure readability and distinguish between different datasets. Additionally, integrating analytics and reporting tools can streamline the process of visualisation, facilitating the identification of significant patterns and trends. This approach not only improves comprehension but also aids in the presentation of findings to stakeholders, ensuring that the data speaks clearly and effectively.
FAQS
What is qualitative data analysis?
Qualitative data analysis involves interpreting non-numerical information, such as text or audio, to identify themes, patterns, and insights that can inform decision-making.
How can I identify themes and patterns in my data?
To identify themes and patterns, read through the data thoroughly, highlight key phrases, and group similar ideas together. Look for recurring concepts that can help you draw meaningful conclusions.
Why is it important to compare my findings against benchmarks?
Comparing findings against benchmarks helps to assess performance relative to industry standards or previous results, allowing for a clearer understanding of where improvements are needed and how effective current strategies are.
What should I consider when setting standards for evaluation?
When setting standards, consider the specific goals of your analysis, industry best practices, the context of your data, and any regulatory requirements that may apply to your field.
How can I create effective charts and graphs for visualising findings?
To create effective charts and graphs, choose the right type of visualisation for your data (e.g., bar charts for comparisons, line graphs for trends), keep designs simple and clear, and ensure that labels and legends are easy to read.