Table Of Contents
Importance of Data Accuracy
Data accuracy plays a critical role in the field of Analytics and Reporting. Accurate data ensures that stakeholders receive reliable insights which guide decision-making processes. Misleading or erroneous data can lead to misguided strategies and wasted resources. In an ever-evolving business environment, maintaining data integrity becomes paramount, as it directly influences the overall performance and reputation of an organisation.
Furthermore, inaccuracies in data can erode trust within teams and across departments. When analytics are not grounded in reliable data, it can lead to confusion and misalignment among employees. By prioritising data accuracy, organisations empower their analysts to provide valuable insights that truly reflect the state of the business. This, in turn, enhances collaboration and fosters an environment of informed decision-making based on trustworthy information.
Ensuring Reliable Reporting
Reliability in reporting is paramount for any organisation that relies on data-driven decisions. Data insights must be accurate and consistent to support strategic initiatives. Reporting professionals ensure that the data collected undergoes meticulous validation processes. They adopt a systematic approach to identify anomalies and rectify potential discrepancies before analysis takes place. This attention to detail is crucial in maintaining trust in the reports generated.
Analytics and Reporting play a vital role in revealing trends and patterns that influence business strategies. By employing robust methodologies, analysts can filter through large volumes of data to deliver insights that are not only actionable but also dependable. Regular audits of data sources and reporting processes help maintain standards of accuracy. Stakeholders rely heavily on these reports for informed decision-making, highlighting the importance of adherence to reliability throughout the analytical process.
Best Practices in Data Reporting
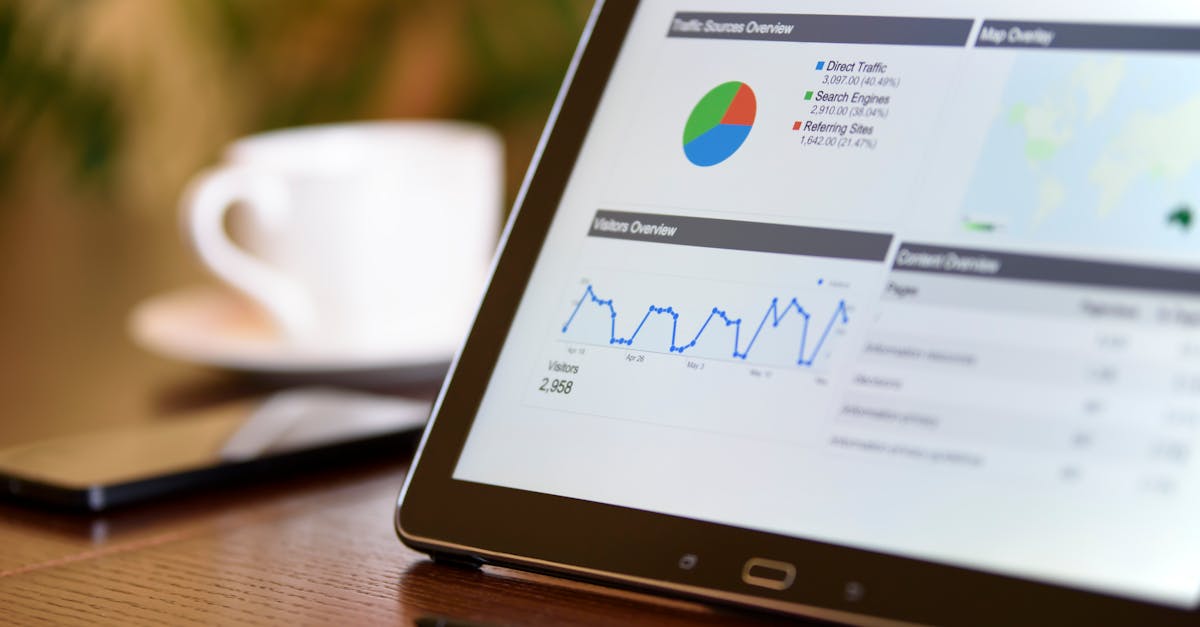
Clear and consistent data reporting is crucial for any organisation relying on data-driven decisions. Best practices in data reporting begin with ensuring that data sources are credible and up-to-date. Consistency in formatting and visual presentation enhances readability. Analysts should standardise their reports, making it easier for stakeholders to understand trends and insights. Regular audits of data can also help identify discrepancies, thereby maintaining the integrity of the analytics.
Effective visualisation techniques can significantly improve the comprehension of complex datasets. By employing graphs, charts, and dashboards, analysts can present vital metrics in an accessible manner. Using interactive reporting tools encourages stakeholders to delve into the data further. Providing a narrative alongside the visuals facilitates a better understanding of the analytics and reporting process. Ultimately, attention to detail in data presentation can lead to more informed decisions across the organisation.
Effective Communication of Findings
Effective communication of findings is crucial for data analysts, as it transforms raw data into insights that can drive decision-making. Analysts must present their findings clearly and concisely, ensuring that stakeholders grasp the implications of the data. This often involves tailoring reports and visualisations to the audience's level of understanding. Utilising storytelling techniques can greatly enhance engagement, making complex data relationships more relatable.
The role of analytics and reporting extends beyond merely presenting numbers. It requires constructing narratives that underscore the significance of the findings within a business context. By emphasising actionable insights, analysts can guide strategic planning and operational improvements. Creating a dialogue around data fosters a collaborative environment where decisions are based on shared understanding rather than solely on statistical outcomes.
Career Pathways in Data Analysis
The field of data analysis offers various career pathways that cater to different interests and skill sets. Entry-level positions often focus on data collection and preliminary analysis, providing a solid foundation in analytics and reporting. As analysts gain experience, they may specialise in areas such as business intelligence, financial analysis, or market research. Continuing education and certifications can enhance professional credentials, making analysts more competitive in a rapidly evolving job market.
With further experience, opportunities for advancement expand significantly. Senior roles may involve leading teams, influencing strategic decisions, and managing complex projects. Professionals proficient in analytics and reporting can transition into managerial positions or leverage their expertise to explore roles in data science or machine learning. Networking within professional organisations and attending industry events can also play a crucial role in career development, helping analysts stay current with trends and technologies.
Opportunities for Advancement
Opportunities for advancement in the field of Analytics and Reporting are abundant, especially as businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making. Analysts can move into senior roles, where they oversee teams and manage complex projects. This progression often involves taking on strategic responsibilities and influencing organisational direction through data insights. Continuous professional development and acquiring advanced skills in analytics tools can further enhance prospects for career growth.
Many organisations offer pathways for analysts to specialise in niche areas within Analytics and Reporting, such as data visualisation or predictive modelling. These specialisations can lead to roles like data scientist or business intelligence consultant. Networking within the industry and participating in professional communities also opens doors to new opportunities, allowing analysts to share knowledge and learn from peers, which can accelerate career advancement.
FAQS
What is the primary role of a reporting and data analyst?
A reporting and data analyst is responsible for collecting, processing, and analysing data to generate insights that help organisations make informed decisions. They create reports that highlight trends, patterns, and anomalies within the data.
Why is data accuracy important in reporting?
Data accuracy is crucial because it ensures that the insights derived from the data are reliable and trustworthy. Inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making and may have significant negative consequences for a business.
What are some best practices in data reporting?
Best practices in data reporting include using clear and concise visualisations, maintaining data integrity, regularly updating reports, and ensuring that findings are tailored to the audience's needs for better understanding.
How can a reporting and data analyst communicate their findings effectively?
Effective communication of findings involves not only presenting data clearly through visualisations and reports but also telling a compelling story with the data. Analysts should focus on key insights and recommendations that are relevant to the stakeholders.
What career pathways are available for data analysts?
Career pathways for data analysts can include roles such as data scientist, business intelligence analyst, and data engineer. Analysts can also advance into management positions or specialise in specific industries, like finance or healthcare.